18 3: Common-Size Financial Statements Business LibreTexts
The main difference is that a common size balance sheet lists line items as a percentage of total assets, liability, and equity, which is different from the normal numerical value. A common size financial statement is used to analyze any changes in individual items when it comes to profit and loss. They’re also used to analyze trends in items of expenses and revenues and determine a company’s efficiency. A common size financial statement is a specific type of statement that outlines and presents items as a percentage of a common base figure. The process of creating a common size financial statement is often referred to as a vertical analysis or a common-size analysis.
Spotting Creative Accounting on the Balance Sheet
Coca-Cola’s gross margin is 63.9 percent of net sales compared to 54.1 percent at PepsiCo. Coca-Cola’s operating income is 24.1 percent of sales compared to 14.4 percent at PepsiCo. Figure 13.8 compares common-size gross margin and operating income for Coca-Cola and PepsiCo.
8: Common-Size Statements

This type of analysis is often used when performing due diligence for an acquisition, a valuation or any other financial transaction. It’s important to note that the common size calculation is the same as calculating a company’s margins. The net profit margin is simply net income divided by sales revenue, which happens to be a common-size analysis. You can measure cash as a percentage of total assets to determine the relative amount of cash the company holds. This calculation is called common-size analysis, which compares the amount of a balance sheet account to total assets. Common-size analysis makes it easier to compare cash balances over time and between companies.
How Common Size Financial Statement Differs from Regular Financial Statements
Owner equity, assets, and liabilities are shown in the financial statement as a percentage of total assets. This type of financial statement makes it simpler for analysts to evaluate the profitability of a company over time. On the debt and equity side of the balance sheet, however, there were a few percentage changes worth noting. In the prior year, the balance sheet reflected 55 percent debt and 45 percent equity. In the current year, that balance shifted to 60 percent debt and 40 percent equity.
3: Common-Size Analysis of Financial Statements
It also allows you to view a horizontal perspective over a period such as the three years that were analyzed in our example. She holds a Masters Degree in Professional Accounting from the University of New South Wales. Her areas of expertise include accounting system and enterprise resource planning implementations, as well as accounting business process improvement and workflow design. Jami has collaborated with clients large and small in the technology, financial, and post-secondary fields. The most significant benefit of a common-size analysis is that it can let you identify large or drastic changes in a firm’s financials.
- This analysis gives the company a heads up if cost of goods sold or any other expense appears to be too high when compared to sales.
- One of the biggest benefits is that it provides investors with information to see changes in the financial statement of a company.
- For example, it could be cash flows from financing, cash flows from operations, and cash flows from investing.
- The same calculation for Company B shows operating profits at 75% of sales (15/20).
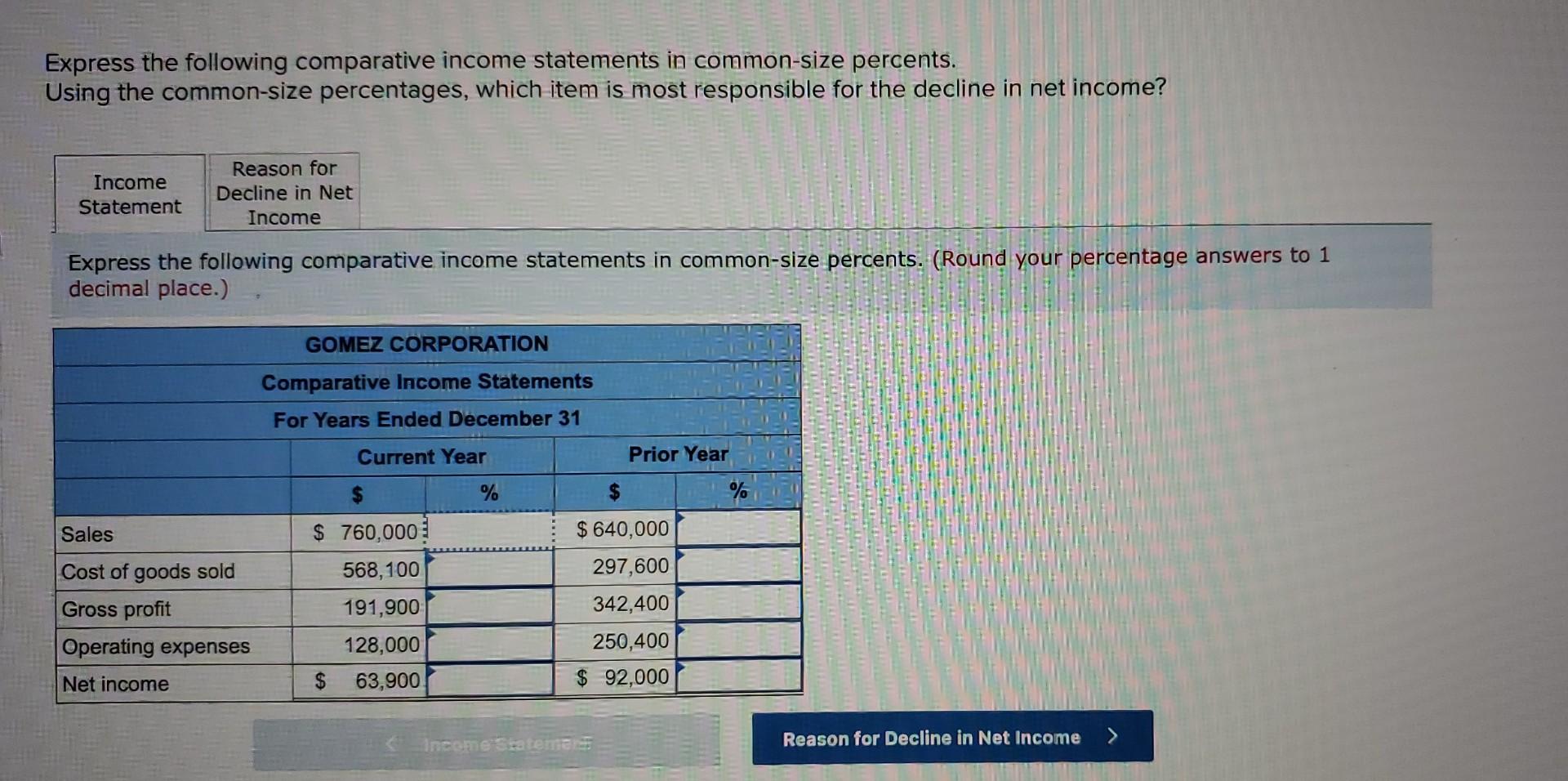
As a result, the financial statement user can more easily compare the financial performance to the company’s peers. For example, you may show merchandise inventory or express the items in common-size percents. accounts receivable as a percentage of total assets. The balance sheet uses this presentation on individual items like cash or a group of items like current assets.
The firm did issue additional stock and showed an increase in retained earnings, both totaling a $10,000 increase in equity. However, the equity increase was much smaller than the total increase in liabilities of $40,000. The remainder of that increase is seen in the 5 percent increase in current liabilities. Common size income statements with easy-to-read percentages allow for more consistent and comparable financial statement analysis over time and between competitors. You would do this for each of the other line items to determine the common size income statement figures. It outlines and reports everything from liabilities, assets, and owner equity as a percentage of the sales or assets.
For Synotech, Inc., approximately 51 cents of every sales dollar is used by cost of goods sold and 49 cents of every sales dollar is left in gross profit to cover remaining expenses. For trend analysis, it’s useful to look at a company’s activity from one time period to the next. For example, inventory might be a much larger percentage of total assets this year, which could mean the company’s chosen slow-moving merchandise needs to match prices with the competition. Also, common-size balance sheets work very well for comparing a company to its competitors or to an industry standard.
Creating this type of financial statement makes for easier analysis between companies. A financial statement or balance sheet that expresses itself as a percentage of the basic number of sales or assets is considered to be of a common size. Common-size analysis, also known as vertical analysis, is the process of constructing a financial statement of a common size. Notice that PepsiCo has the highest net sales at $57,838,000,000 versus Coca-Cola at $35,119,000,000. Once converted to common-size percentages, however, we see that Coca-Cola outperforms PepsiCo in virtually every income statement category. Coca-Cola’s cost of goods sold is 36.1 percent of net sales compared to 45.9 percent at PepsiCo.
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are based on consistency and comparability of financial statements. A common size income statement makes it easier to see what’s driving a company’s profits. The common size percentages also help to show how each line item or component affects the financial position of the company.
Many items in the cash flow statement can be stated as a percent of total sales, similar to an income statement analysis. This can give insight into several cash flow items, including capital expenditures (CapEx) as a percent of revenue. Based on the accounting equation, this also equals total liabilities and shareholders’ equity, making either term interchangeable in the analysis. It’s also possible to use total liabilities to indicate where a company’s obligations lie and whether it’s being conservative or risky in managing its debts. A common-size financial statement displays line items as a percentage of one selected or common figure.
GST calculator Online GST calculator
To calculate IGST, just multiply the taxable amount by the appropriate GST rate. For an intra-state transaction, you’ll need to...
Future Value Annuity Calculator: Calculate FV of Equal Cash Flows
The monthly bills such as rent, car payments, and cell phone payments are done at the start of the month. The insurance amount payment...
What are Post Journal Entries? Definition Meaning Example
It ensures that every transaction is recorded correctly, providing a reliable basis for financial analysis and decision-making. When...













 Thăng Long Đạo Quán 2021. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy
Thăng Long Đạo Quán 2021. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy